✓ Indicators
✔️ INDICATORS |
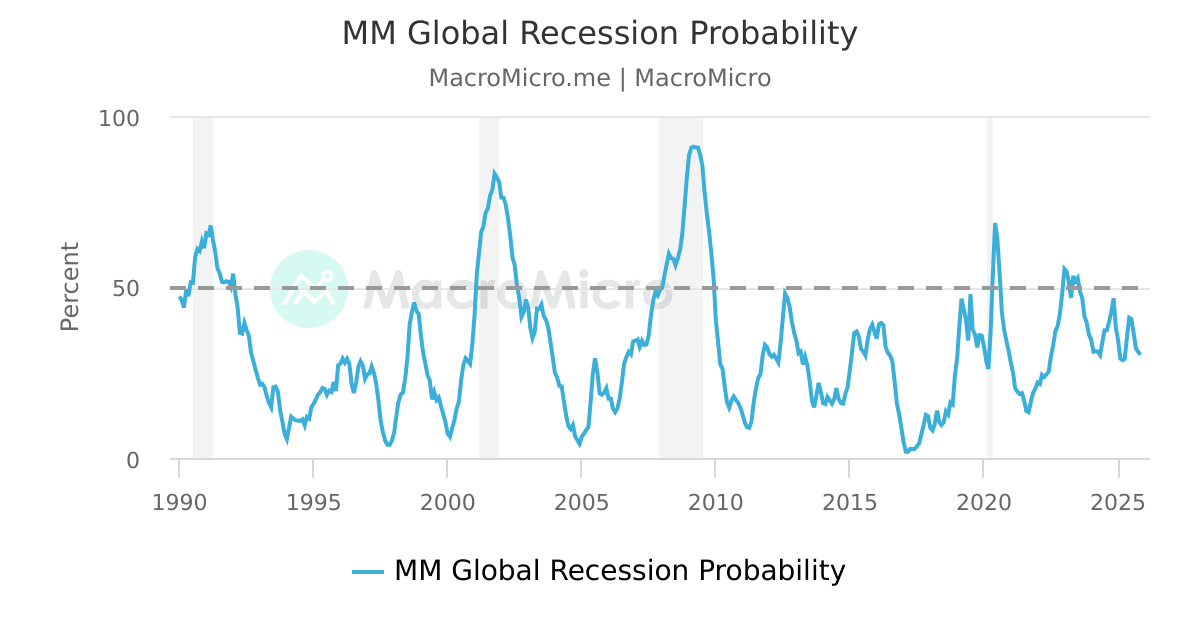
In this section, there are some of the main indicators to assess the trend of stock markets. The majority of these indicators refer to the U.S.A. exchanges since they are by far the largest in the world having a 45-50% share of the overall capitalization.
MARKET EXTENSION AND INTENSITY: | ||||||||
MSCI FORWARD P/E | ||||||||
STOCK EXCHANGE MM FUNDAMENTAL (MMF) INDICES: | ||||||||
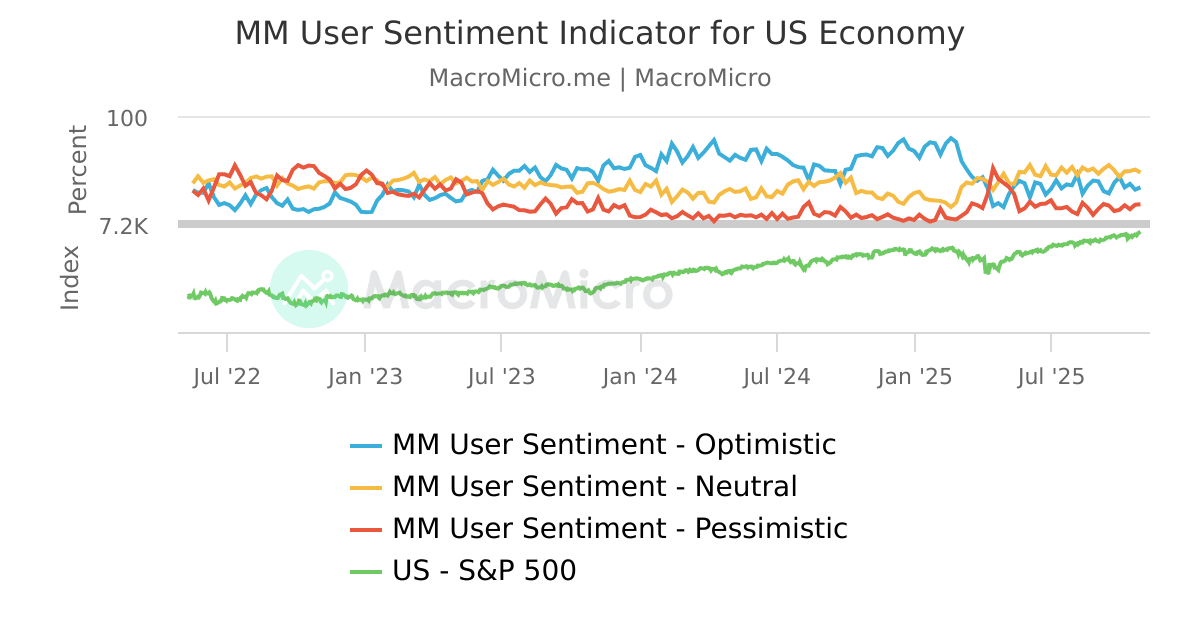
MARKET SENTIMENT AND CONFIDENCE: | ||||||||
CONSENSUS ON EARNINGS / REVENUES GROWTH: | ||||||||
EARNINGS AND REVENUES REVISION: | ||||||||
BBB Corporate Yield - 3m Treasury Yield
Corporate Profit Growth Rate
CBOE S&P 500 3-Month Volatility Index
Average Investor Allocation to Equities (AIAE)
Chicago Fed National Financial Conditions Index
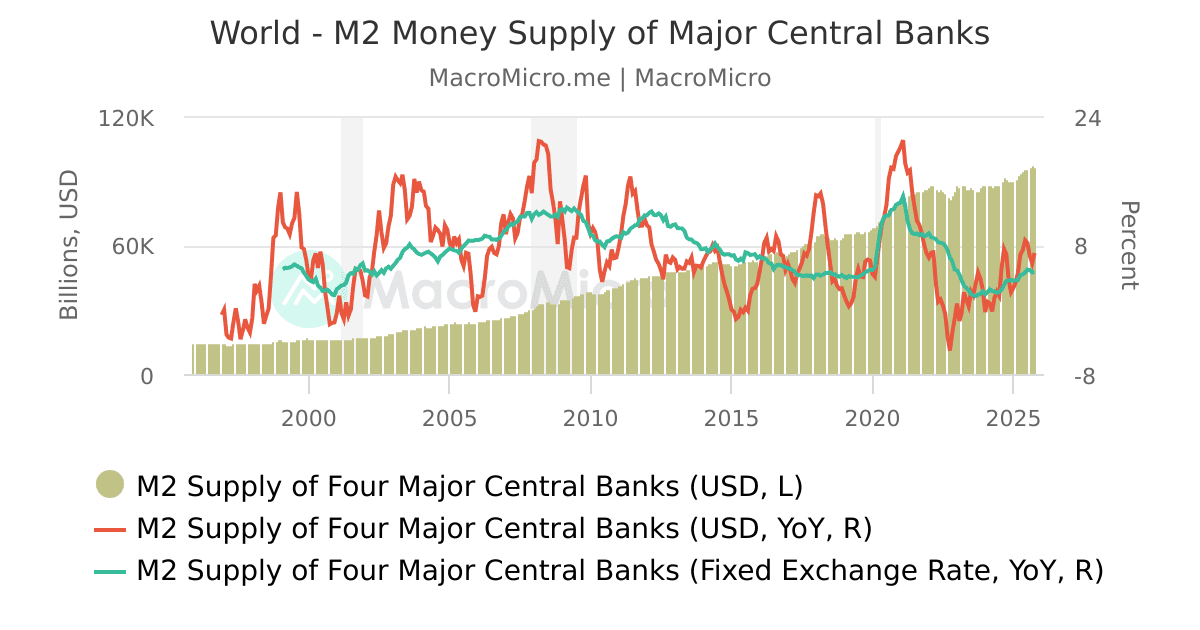
S&P 500 divided by Money Supply M2





US - Net Treasury International Capital Flows
source: tradingeconomics.com
Euro Area Capital Flows
source: tradingeconomics.com
DESCRIPTION OF SINGLE INDICATORS
| New Highs and New Lows - New Highs/Lows Oscillator and Ratio | |
US - S&P 500 Price vs. PE Ratio: The difference between the S&P 500 index price and its P/E ratio, both on year-on-year basis, reflects the market's expectations for S&P 500's EPS. When the difference is above 0: If stock prices are growing faster than the P/E ratio, the upward revisions of earnings are in line with the increase in valuation. If the P/E ratio drops faster than price, the decrease in valuation is overestimated compared to the downward revisions of earnings. When the difference is below 0: If the P/E ratio grows faster than price, the upward revisions of earnings are insufficient compared to the increase in valuation. If stock prices drop faster than the P/E ratio, the decrease in valuation is underestimated compared to the downward revisions of earnings. | |
